What are the metal cutting capabilities of a fiber laser cutter depending on its power?
Currently, the market offers fiber laser cutters for metal with different power capacities. Until recently, the 1500W laser generator (or resonator) was common for cutting, but it was discontinued in 2024 (although it is still available for laser welding applications). This follows the same path as the 1000W model, which disappeared in 2021.
Today, the minimum cutting power for metal available on the market is 2000W. Within the “Entry Level” range, the most popular models are 3000W, followed by 6000W, 12000W, and 20000W.
When it comes to laser generator brands, the most popular ones today are:
- MAX Photonics
- Raycus
- RECI
To these we can add historic and well-recognized brands like IPG and Coherent, which once set the standard. However, in recent years Chinese brands have consolidated themselves as global leaders in sales and production, even gaining acceptance in markets that were previously resistant to them, such as the United States.
Now, many people ask: do machines manufactured in China cut the same as those from European, Japanese, or North American brands? The answer is yes—they cut the same.
Why can’t I always cut what I should be able to cut?
The most common metals for laser cutting are stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and brass (a copper-zinc alloy). However, there are several factors that may prevent you from achieving the results promised by the manufacturer:
- Metal variations
Every alloy has different resistance to heat and laser cutting. Even within the same grade, the composition may vary depending on the manufacturer. For example, a 304 stainless steel made in China may behave differently during cutting compared to one produced in the United States. - Dirty or coated surfaces
Rust, dirt, or coatings affect performance. If the material is not clean, it will be very difficult to achieve the cut shown in the manufacturer’s catalog. - Quality and type of cutting gases
Assist gases are critical in the process.- Nitrogen and oxygen: Ideally, purity levels should be 99.9% or higher. Some suppliers even offer special formulas for laser cutting. If industrial or medical-grade gases are used, the quality may not be sufficient.
- Compressed air: At least 240 PSI is recommended for low- and mid-power systems, and over 350 PSI for equipment above 6000W. The air must also be dry, the compressor should be located no more than 5 meters from the machine, and the system must include a dryer and multiple filters to prevent condensation or impurities.
- Misaligned or poorly maintained cutting head
If the head is dirty or worn in components such as lenses, collimator, protective glass, or nozzles, the cut will be affected. Even minimal dirt can lead to major damage and higher consumable costs.
Reference tables: how accurate are they?
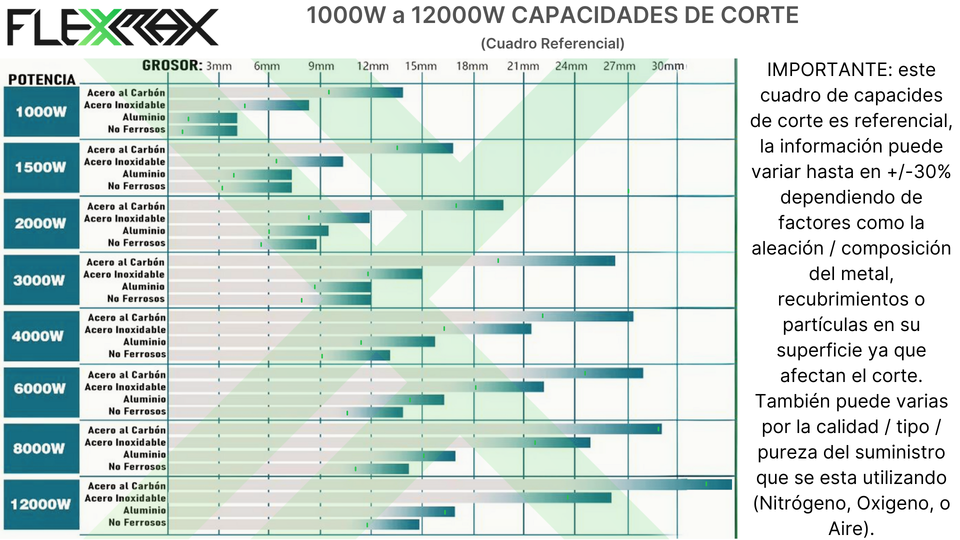
Tables showing cutting capabilities by power—1000W, 1500W, 2000W, 3000W, 4000W, 6000W, 8000W, and 12000W—are based on laboratory tests under optimal conditions.
In practice, those conditions are rarely met in daily production. That’s why, in the chart we share below, we added green markers on each bar with our own results from real production tests.
These values represent, in our opinion, the maximum levels that can be consistently achieved, always considering there is a margin of error influenced by the factors mentioned above.



Member discussion